Art Cam Create a Curved Back on a Piece
Introduction: Relief Editing
This example shows how to employ some of the relief editing tools.
Functions
![]() Ready Model Size - Set the real physical size of the model
Ready Model Size - Set the real physical size of the model
![]() Smooth Relief - Utilise smoothing filter to the whole relief or a specific area
Smooth Relief - Utilise smoothing filter to the whole relief or a specific area
![]() Texture Relief - Utilise 3D texture to the whole relief or a specific area
Texture Relief - Utilise 3D texture to the whole relief or a specific area
![]() Scale Relief Height - Scale relief heights in Z
Scale Relief Height - Scale relief heights in Z
![]() Smooth Sculpting - Interactive Sculpting tool to smooth areas of the relief
Smooth Sculpting - Interactive Sculpting tool to smooth areas of the relief
![]() Smudge Sculpting - Interactive Sculpting tool to re-model relief similar dirt
Smudge Sculpting - Interactive Sculpting tool to re-model relief similar dirt
![]() Deposit Sculpting - Interactive Sculpting tool to add material to the relief
Deposit Sculpting - Interactive Sculpting tool to add material to the relief
![]() Carve Sculpting - Interactive Sculpting tool to remove fabric from the relief
Carve Sculpting - Interactive Sculpting tool to remove fabric from the relief
![]() Envelope Distortion - Select a floating bluish relief clipart to re-create, distort, and paste it along a bend
Envelope Distortion - Select a floating bluish relief clipart to re-create, distort, and paste it along a bend
The following tin be managed from the Relief Layers department.
![]() Add a new Relief Layer to the model
Add a new Relief Layer to the model
![]() Import a new Relief Layer from a file
Import a new Relief Layer from a file
![]() Export the selected/highlighted Relief Layer
Export the selected/highlighted Relief Layer
![]() Duplicate the selected Relief Layer
Duplicate the selected Relief Layer
![]() Transfer the selected Relief layer to the opposite side (Back Relief Layer)
Transfer the selected Relief layer to the opposite side (Back Relief Layer)
![]() Create a new Bitmap Layer from the selected Relief Layer
Create a new Bitmap Layer from the selected Relief Layer
![]() Delete the selected Relief Layer from the model
Delete the selected Relief Layer from the model
![]() Merge (combine) the visible layers to form a new Relief Layer
Merge (combine) the visible layers to form a new Relief Layer
Pace 1: Example 6-one
Step 2: Example 6-2
Step 3: Texture From Image Tutorial
i Open Model - stone_pattern.png
- Width = 12"

two Select the stone_pattern Bitmap Layers in the Project Tree
iii Create Relief Layer (from bitmap layers) ![]()
- New Elevation = 0.15"
4 Polish Relief - ane pass
Next you are ready to save your new texture past into your clipart binder
5 Open up Relief Clipart Library
- Chose to view the Custom Reliefs clipart folder
- Using your left mouse push select in your project tree, stone pattern Relief Layer you have just created
- And drag into the Relief Clipart Library

Step 4: Relief Layer Badge Tutorial
1 Open up Model Relief Layer Badge.fine art
2 Expand the Forepart Relief Layers section of the Project Tree

3 Hide all Relief Layers past clicking on the twin low-cal seedling ![]() adjacent to the chief branch Front Relief
adjacent to the chief branch Front Relief
To ameliorate understand layers, employ the light bulbs to hide and testify dissimilar relief layers. This volition assist demonstrate how they interact together. Hide all the layers when finished
4 In the Project Tree, click on the calorie-free seedling ![]() to show the Laurel Relief Layer and the Flower3 Relief Layer
to show the Laurel Relief Layer and the Flower3 Relief Layer
five Show the Base Relief Layer and notation how it embosses the other reliefs
6 Show the ArtCAM Relief Layer to finally display the text
As demonstrated, a Relief Layer can exist switched on/off as required by clicking the next light seedling icon. Any Relief operations assigned to a Relief Layer that is switched off will be temporarily hidden from the model.

7 Hide the Base of operations Relief Layer to see the result


eight Toggle the Base layer back on merely Hibernate the Flower3 Relief Layer
nine Make the ArtCAM Relief Layer active by clicking on its proper noun to highlight it.

10 Select New Relief Layer ![]() from the lower Project Console.
from the lower Project Console.
The new Relief Layer is created directly above the active Relief Layer.
11 Select the new Relief layer and rename it to Panthera leo from the lower Project Panel

12 From the Relief pull down menu, chose Import, followed by Import to load in an existing relief ![]()
13 Choose Lionhead.rlf from the ArtCAM data folder
14 No changes are required and then Click Paste on the Transform course
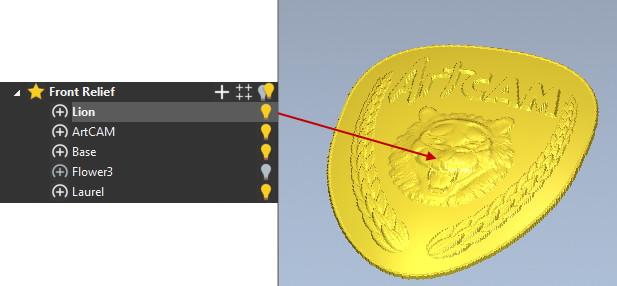
Relief Layers can exist utilised to organise work, simplify adjustments, and easily experiment with different variations.
15 Create another New Relief Layer and rename information technology to Banner.
xvi Open the Relief Clipart Library from the Relief creation toolbar ![]()
- In the pull down listing at the top, choose the Banners Library.
- Click on Banner1 to select and import it

17 Employ the Transform tools to resize and position it suitably or use the parameters suggested below.
- Press F9 to centre in the model
- In Scale and Size, enter a new Scale of 50% with all sizes linked and then click Utilize
- In Origin position, Enter a value of ii in Y and then Apply (note ArtCAM model is in imperial units)
18 At the top of the Form, Click on More Options icon ![]()
- For now, ignore the Paste Combine Mode but enter a value of 0.one for Meridian (start height).
- Select Paste.
The banner appears to be sitting overlapped with the rest of shield. This can be inverse by adjusting the Relief Layer Combine style. The Combine mode dictates how the Relief Layers interact with each other. Currently all the Relief Layers are on the Add together Combine mode. If the problem layer, in this case, the new banner layer is changed from Add to Merge High, it will blend in with the relief of the design.

xix Make sure the Imprint Relief layer is agile
20 In the lower parameters section on the Project panel, alter the Combine mode from Add to Merge Loftier

The imprint at present blends in with all the other Relief Layers.
The Relief layers are effective from top to bottom. The Combine way of the top Relief Layer affects everything below it. The Combine mode of the bottom Relief layer affects nothing.

Step v: Grapevine Tutorial
A customer has asked us to reproduce an existing molding. He has indicated to united states that it doesn't need to be an exact duplicate, simply if the end results produced in ArtCAM were like to the original, then that would be fine.

Getting the Design into ArtCAM
There are several different ways that an ArtCAM user could go about getting the design vectors into the software.
The first method, the designer would visually inspect the piece of moulding and with role in hand would build the vectors in ArtCAM by eye. This is actually the fashion that the vectors we will be using accept been created.
A 2d method to get this information into ArtCAM could be, to accept a digital photograph of the moulding and utilise it as a template. The photo could exist opened in ArtCAM and the user could trace the necessary outline vectors. This method may be a bit easier for someone who may not exist very artistic. Using a digital photo would give the user the ability to follow the outlines of the pic and basically trace information technology.
The third possibility could be to use the plastic transparency canvass on the Wacom Pressure sensitive tablet and manually trace the outline of a printed photograph. This option is similar to the second method but may use more to someone who may not have the image in digital format. If it was a small 5" 10 7" photo it could be diddled upward in size before it was used for tracing, this is of class providing the size of the photo stays within the limits of the Wacom tablet's transparency envelope.
Analysing the Design Vectors of the Grapevine
If you look and encounter how the designer of this file has ready up the design vectors yous should find a few things.

The vectors for each modelling section are on separate layers, making it much easier to work with.
You lot tin see that in that location are several separate vector entities that stand for the unlike branches of this vine. These parts of the vine take been separated out so that there is a certain consequence achieved when the vine is built. If these areas were all combined into ane main branch and then the results of building the vine shape would not expect natural or organic. What would end upwards happening is the large mutual area where the main vine and the smaller vine meet upwardly would have a very balloon like and bubbly appearance. The only way that a user would know this data would be from trial and error and/or from experience. Having the small branches of this vine set upward the manner they are is going to give u.s.a. the most natural looking effects possible with the least amount of relief modelling attempt. ArtCAM contains useful tools that we can use to get in and change these areas to look more natural after we have built them into 3D.
If you select the circular vectors representing the grapes, you will observe that they have not all been grouped together as i entity. Random diameter circles inside the agglomeration take been grouped together in order to requite the relief of the grapes a varying effect. This varying consequence for the grapes is achieved by the divergence in the diameter of the various circular vectors.
The style it has been set is that the different groups take been assigned unique characteristics for relief modelling and since the circles have varying diameters they will individually reach unique heights. The way that ArtCAM works is, when using the Shape Editor to build reliefs the software associates width with height, therefore the wider something is the higher that it is going to take to be in 3D infinite so that information technology looks proportional.
The foliage has 2 design vectors showing the shape, there are other vectors on some other layer that will be used to reach an underlying sweep.
1 last item to pay attention to in this blueprint is the resolution. Resolution is a very important factor of an ArtCAM job. The resolution is set at 1991 X 663 pixels; commonly the rule of thumb (depending on chore sizes and relief modelling technique) is that the shortest side of the model should comprise approximately 1000 pixels. Having said this you tin can see that the shortest side of this job merely contains 663 pixels. The reason for this is that the entire piece is going to be modelled using vector modelling. When yous are doing vector modelling it is possible to piece of work with a resolution that is approximately 1/3 less than what you would normally use if you lot were colour modelling. The 1000 pixel rule outline above is for colour modelling so that is why you are seeing a lower resolution then usually recommended.
Strategy for Building the Grapevine
Every bit with most projects information technology is important that before you brainstorm to piece of work that you think about how you lot are going to get to the final result. The aforementioned rules apply to ArtCAM, before we start to build our relief, we should take a few minutes to look at it and think well-nigh the best style to build our design into a 3D relief.
As in many cases with ArtCAM, when you are going to be building a design that contains several parts or pieces, it is best to try and isolate the smaller parts and build these in carve up relief layers.
For the Grapevine the program is going to be as follows:
- Create three unlike relief layers for Grape Leaf, Primary Vine and Grapes and construct them in individual relief layer.
- Build the leaf is several steps. Since the Shape Editor is not going to give us enough command over how the shape is built, the designer has decided to utilise one of the more than user definable relief modelling tools; Extrude.
- The extrusion role will be used to build the underlying shape of the leaf.
- Build up the vine shape using the chief vine vector as well equally the branch vectors.
- Since the piece needs to look equally natural and organic as possible we will accept to do some sculpting on sure areas of the relief.
- The tertiary relief that is going to be built will be the grapes. The grapes should be quite straightforward and easy to build since nosotros volition just use the Shape Editor to build the shapes.
- Once building the individual relief is washed all the layers will exist made visible.
Building the Grapevine
1 Open up the file Grape-Vine.art
This tutorial is based in the default ArtCAM function layout. If you lot accept customised your layout and wish to return to the standard, from the Window pull downwards card cull Reset Layout.
2 Toggle Vector Visibility to on to show vectors in the 3D View
Grape Leaf

1 From the Projection Tree, show the Leaf and Structure Vector Layers, hide all other Vector Layers
ii Brand 3D Leaf the agile Relief Layer
The Leaf layer contains the vector representing the size and shape of the leaf.
The Construction layer has additional vectors used to assistance us in building the underlining relief.
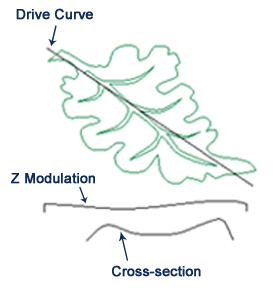
iii Open up the Extrude function from the flyout toolbar located on the Relief Creation toolbar
4 In the model area pick the straight vector that runs through the leaf for the drive curve and click Select button in the panel next to Bulldoze curve
five Check the Employ every bit centreline box
vi Pick the vector that represents the contour (Cross-Section) for this extrusion, click the Select button next to Start Profile
7 Check the Invert bend in Z box to brand sure that the hash marks are on the inside of this vector shape
viii Pick the vector that represents the Z modulation and click the Select button next to Z Modulation
nine Make sure that Add together is the option that is selected and and so click the Apply button to build the underlying shape of the Grape Leaf
ten Close the Extrude panel
Find that the underlying shape for this foliage that has been extruded is larger than the bodily foliage itself. This is a pretty common technique used for relief modelling in ArtCAM where the underlying shape is created much larger than needed and and then the required area gets trimmed out.
11 Select the vector outline of the foliage and press the Zippo Outside Vector office
This should trim out the shape of your foliage.
12 With the leafage outline vector yet selected, press F12 to open up the Shape Editor
13 Click Add together in the Shape Editor window so Close
- Dome, Bending=-5º, Offset Height=1mm (0.04"), Apply
This will add the concave shape of -5º with a small start peak to the leaf. You will non run across much of a alter when the vector attributes are added to the existing relief. The leafage will get a chip higher and it will besides provide a bit more than of a dish shape to the leafage. Past doing this we are trying to add a more than natural await.
14 Select the vectors that correspond the vein particular for the leaf
15 Press F12 to open the Shape Editor
- Add together Dome, Angle= -25º, Start Meridian= -0.5 mm (-0.02") , Apply
xvi In the Project Tree, click on the lite seedling next to 3D Leaf to hide the 3D Foliage Relief Layer
Chief Vine

ane Brand 3D Vines the active Relief Layer
2 Show the Vines Vector Layer, hibernate all other Vector Layers
3 Select the vine vectors one past one, open the Shape Editor with F12 and Add or Merge high. The values are already applied to the vector shape;
- Main vine (Dome 68º, Offset Top=1mm (0.05"), Add), Use
- 1st and 2nd co-operative (Dome 83º, Kickoff Top 1mm (0.04"), Merge High), Use
- 3rd branch (Dome 70º, Start Acme=1mm (0.04"), Merge High), Utilise
- fourth branch (Dome 83º, Start Elevation=1mm (0.04"), Merge High), Apply
- fiveth branch (Dome 70º, Start Height=1mm (0.04"),Merge High), Apply
Observe the creases in the areas where the branches take been merged into the main vine. Ideally, we want to smooth these areas in social club to make the vine look more than organic.
iv Zoom into the outset area where you tin meet the creases
5 Activate the Smoothen Sculpting tool
6 In the Tool Setting Panel, set the following:
- Radius = 25
- Forcefulness = 50
- Smoothness = 100
In the Mask area, check the Cloth Rubber Plane and enter in a value of .025mm (0.01")
By making adjustments to the Mask section of the Sculpting panel, we ensure that when nosotros are smoothing the relief, the smooth tool will non impact the background (zero airplane), causing a radius at the edge where the relief meets the zero plane.
7 While using the Smoothen tool, vary the diameter and strength of this tool accordingly to accomplish the desired results
8 Smooth the creases where the smaller branches attach to the larger branch
Basically we simply want to get rid of the creases and make the vine look more natural. Individual results may vary.
To zoom in & out yous need to hold the Alt key downwards while using the mouse equally you would in a regular 3D view, or use the icons at the pinnacle of the screen.
9 Click on the calorie-free bulb adjacent to 3D Vines to hibernate the 3D Vines Relief Layer
Grapes
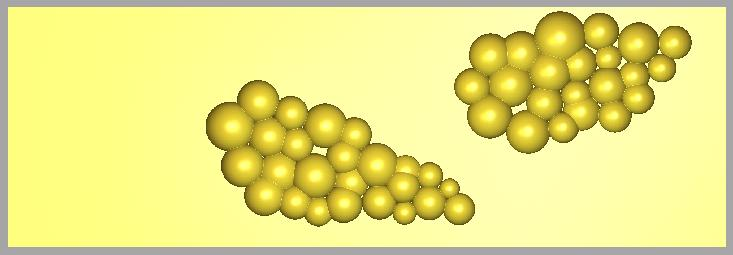
i Make 3D Grapes the agile Relief Layer
2 Bear witness the Grapes Vector Layer, hide all other layers
3 Select the different groups of circles that represent the grapes and apply the Shape Editor to build these shapes and utilize Merge Highest. The values are already applied to the vector shape;
- 1st ready (Dome 86º, Commencement Height= 3 mm (0.thirteen"), Merge High), Apply
- 2nd set (Dome 80º, Start Height= 2 mm (0.11"), Merge High) , Apply
- 3rd set (Dome 89º, Start Height= 1 mm (0.06"), Merge High) , Use
- ivth gear up (Dome 68º, Showtime Pinnacle= ii mm (0.x"), Merge High) , Apply
Apply the Merge High option then that the grapes are composite into one another.
It can be useful to employ the preview Relief Layer office if working from the 2nd view to track the progress of your relief in the 2D view. Doing this will display an interactive greyscale of the areas every bit they built.
Viewing Combined Reliefs
Now that we accept built all of the pieces for our finished part we can now bring them all together.

iv Testify all Relief Layers
v Toggle Vector Visibility to hibernate the vectors in the 3D View ![]()
6 Relieve the finished ArtCAM files as Finished Grape Vine.art
The design is now complete and ready for machining.
Step half dozen: Example 6-3
3 People Made This Projection!
Recommendations
Source: https://www.instructables.com/Relief-Editing/
0 Response to "Art Cam Create a Curved Back on a Piece"
Post a Comment